Development of electrochemical biosensors for rapid detection of inflammatory molecules: on-site detection of inflammatory biomarkers for diagnostic tests and health monitoring by low-cost, simple-to-manufacture and user-friendly point-of-care immunosensors.
The development of low-cost and disposable biosensors that permit a swift and reliable response without the usage of expensive instrumentation and time-consuming procedure are nowadays gaining an increasing interest. Novel point-of care (POC) biosensors can improve the timely recognition and therapeutic monitoring of inflammatory diseases. These devices provide various advantages over labour- and time-intensive traditional methods, such as faster screening, improved sensitivity and specificity, reduced cost, good efficiency, and the capacity for on-site detections.
By utilizing diverse capture and detection elements, specific to different biomolecules, these biosensors enable the determination of a panel of biomarkers or the analysis of complex biological samples in a high-throughput manner.
The dysregulation of IL-6 signaling is particularly implicated in the pathogenesis of numerous inflammatory pathologies, ranging from chronic inflammatory diseases to autoimmune disorders.
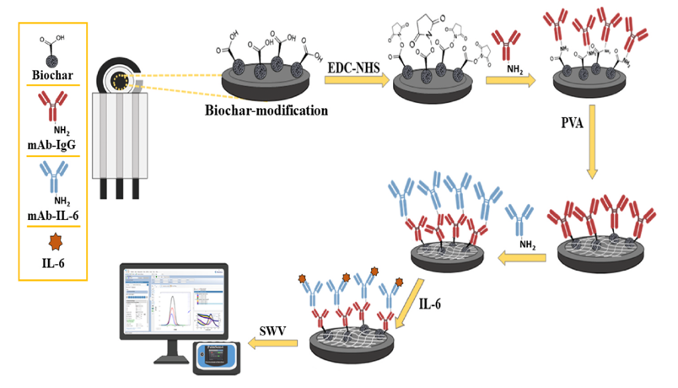
Schematic diagram of the fabrication steps and detection of the IL-6 immunosensor. Biosensors and Bioelectronics 213 (2022) 114467
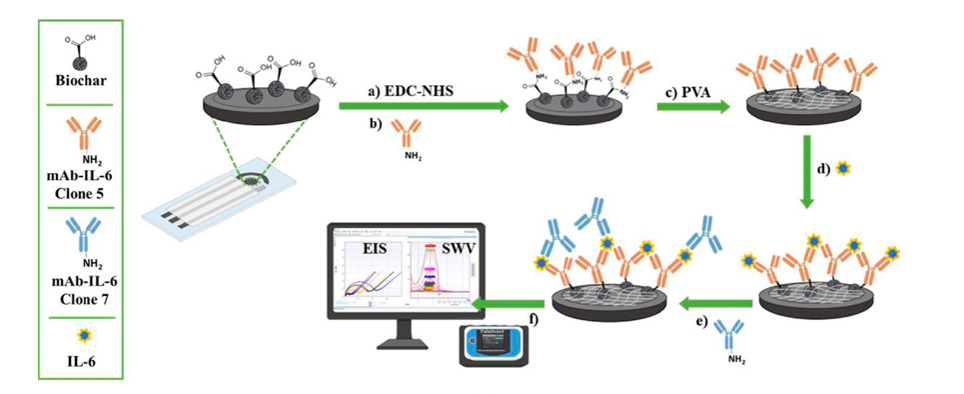
Diagrammatic representation of the fabrication procedures and detection of the IL-6 immunosensor. In (A) and (B) the carbodiimide-mediated amide coupling reaction to immobilize a specific IL-6 antibody (mAb-IL-6-Clone 5) onto biochar-modified screen-printed electrodes. In (C) the backfilling step using PVA and (D) the immunocomplex formation. In (E) and (F) the sandwich formation after adding a second primary antibody (mAb-IL-6- Clone 7) and the electrochemical detection, respectively. Frontiers in Chemistry 10.3389/fchem.2023.1251360
The sensor architecture, due to its simplicity and versatility, is suitable to be repurposed in the detection of many medically relevant diagnostic biomarkers by simply changing the analyte-specific bioreceptor.

